Mastering Agile Metrics: A Guide to Driving Efficiency and Value
By Ron Smith SPC
Agile project management is all about flexibility, efficiency, and delivering value to customers. But how do you measure success in such a dynamic environment? Understanding the right metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for any Scrum Master, Product Owner, or team member venturing into the Agile world. In this post, we will explore the most relevant Agile metrics that help in tracking the progress and success of Agile projects.
1. Velocity: The
Pace of Progress
Velocity is a fundamental metric in
Agile. It measures the amount of work a team completes during a sprint. This is
typically calculated in story points or hours. Understanding velocity helps in
future sprint planning, as it gives a realistic view of the team’s capacity.
However, it’s important not to fall into the trap of comparing velocities
across teams, as each team's working dynamics and story point assessment can
vary greatly.
Velocity is not just a measure of quantity but also a reflection of a team's consistency and predictability. Over time, tracking velocity can reveal patterns in team performance, such as how external factors or changes within the team affect their output. This understanding can lead to more accurate planning and a better grasp of the team's capabilities. It's essential, however, to emphasize that velocity is a tool for the team's internal use and should not be used as a performance metric by management.
2. Burn-down and
Burn-up Charts: Visualizing Progress
Burn-down and burn-up charts are
excellent for visualizing the progress of a sprint or a release. A burn-down
chart shows how much work is left to be done, while a burn-up chart displays
the amount of work completed over time. These charts are great for identifying
any deviations from the plan early on.
These charts are not
only about tracking; they are also communication tools. They provide a clear
and immediate visual representation of the team's progress to stakeholders and
team members alike. Regularly reviewing these charts can foster transparency and
open discussions about any impediments or changes needed in the sprint. They
are particularly useful in meetings and sprint reviews, offering a snapshot of
where the team stands in relation to their goals.
.
3. Sprint Goal
Success Rate: Aligning with Objectives
The Sprint Goal Success Rate is a
simple yet powerful metric. It measures how often the team meets the sprint
goal. This aligns the team's efforts with the sprint's objectives and
encourages them to focus on delivering value rather than just completing tasks.
Achieving sprint goals
consistently indicates a well-functioning Agile team with a clear understanding
of its capacity and priorities. It also reflects on the team's ability to
negotiate and refine sprint goals that are realistic and attainable. This metric
encourages a culture of commitment and focus, as the team collectively strives
towards a shared objective, understanding its importance in the larger context
of the project.
4. Lead Time and
Cycle Time: Efficiency in Workflow
Lead time measures the time from the
customer's request to the delivery of the product or service. Cycle time, on
the other hand, tracks the time it takes for your team to complete work items
from the start to the finish. These metrics are vital for understanding the
efficiency of your workflow and identifying bottlenecks.
Analyzing lead and cycle
times can unveil insights into process efficiencies and the impact of work
practices on project timelines. By identifying where delays typically occur,
teams can implement targeted improvements. For instance, a long lead time might
indicate challenges in backlog management or initial requirements gathering.
Reducing these times is often a clear indicator of process improvement and
enhanced team efficiency.
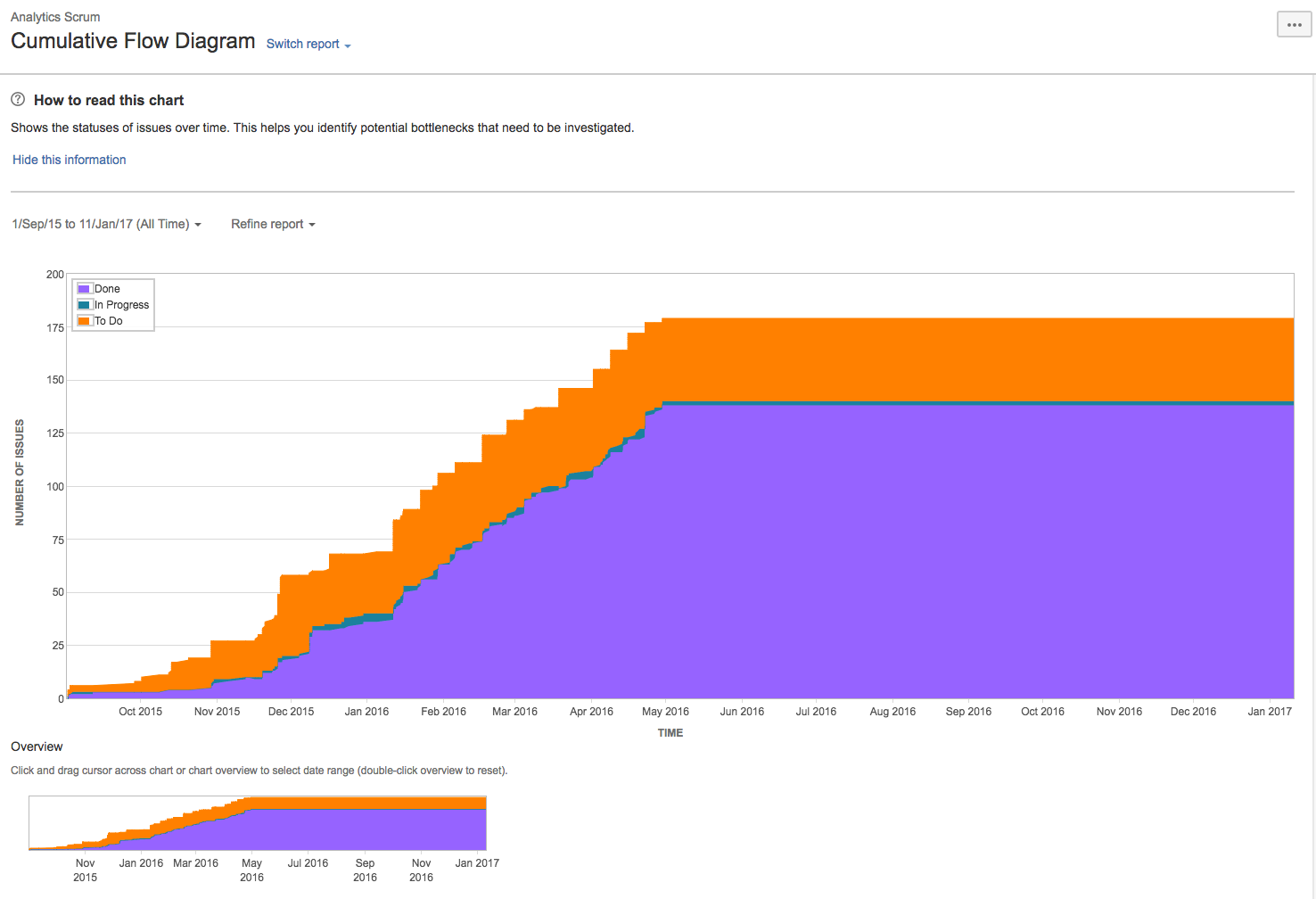
5. Cumulative
Flow Diagram (CFD): Tracking Work in Progress
A Cumulative Flow Diagram provides a
visual representation of the various stages of work items in a given period. It
helps in identifying bottlenecks and ensuring a smooth flow of work. It's an
excellent tool for managing work in progress and ensuring that the team is not
overburdened.
CFDs help in maintaining a balanced workload and preventing bottlenecks. By monitoring the number of items in different stages, teams can quickly identify issues, such as too many items in 'testing' or 'review', indicating a potential resource allocation problem. It encourages teams to adopt a more holistic view of their workflow and strive for smoother transitions between stages.
6. Escaped
Defects: Quality in Delivery
The number of defects or issues that
'escape' into production is a critical quality metric. It reflects the
effectiveness of your testing and quality assurance processes. Keeping escaped
defects low is crucial for maintaining customer trust and satisfaction.
Monitoring escaped defects also serves as a feedback loop for the development process. It helps in pinpointing weaknesses in the testing stages or in the user story definitions. Reducing these defects over time is indicative of improving quality controls and a better understanding of user needs. It’s a metric that resonates well with client satisfaction and product reliability.
7. Happiness
Metric: Team Satisfaction
While not a traditional KPI, the
happiness metric is gaining traction in Agile environments. It’s a qualitative
measure of team morale and satisfaction. Regularly checking in with your team
about their happiness can give insights into the health of the team dynamics
and predict future performance.
The happiness metric can be a leading indicator of future performance and team health. Teams that score
high on happiness are often more collaborative, innovative, and resilient to
stress. Regularly addressing and acting upon factors that affect team happiness
can lead to improved productivity and a more positive work environment.
8. Engagement
Metrics: Customer and Stakeholder Involvement
In Agile, customer and stakeholder
engagement is key. Tracking their involvement in reviews, feedback loops, and
planning sessions can provide valuable insights into the project's alignment
with customer needs and expectations.
Engagement metrics are
pivotal in Agile projects, where customer feedback and iterative development
are key. High engagement levels typically correlate with a product that more
accurately meets user needs and expectations. Tracking these metrics can also
highlight areas where stakeholder involvement could be improved, ensuring that
the final product aligns closely with client expectations and market demands.
Photo by GR Stocks on Unsplash
Agile metrics are about more than just measuring performance. They provide insights into the health of your Agile process, team dynamics, and customer satisfaction. As a new Scrum Master or an Agile practitioner, understanding and effectively using these metrics can vastly improve your team’s productivity and project outcomes.
By focusing on these key metrics, you
can ensure that your Agile journey is on the right track, delivering value to
customers and creating a fulfilling work environment for your team. Remember,
these metrics are tools to guide you, not just numbers to report. Use them to
foster a culture of continuous improvement and excellence in your Agile
practice.
About the Author
Ronnie S. Smith SPC, with a career marked by
significant Agile contributions since 2003, led a transformation at AKFSI and
held a trumpeted Sr. Scrum Master role at Bank of America, establishing himself
as a recognized authority in Agile methodologies. As a SAFe trainer with 13
Agile certifications and 8 SAFe enablements, Ron has been instrumental in
advancing Agile practices. His book, "Waking up Agile," due for
release soon, promises to extend Agile concepts beyond the workplace, offering
insights for applying these principles to everyday life. Available for
pre-order orders@wakingupagile.com











Comments
Post a Comment